푼 문제는
참고로 숙제 문제는 5,7,9,10,11,19 + Problem 3.
2. In analogy to Prop 2.5, prove that if
증명:
(1)
이다.
(2) 그러므로 그냥
이 때
그러므로, 충분히 1에 가까운
이다. 따라서 원하는 것이 보여진다.
6.
(a) There exists a positive continuous function
(b) If
증명:
(a) 다음 그래프를 가지는 함수

그러면
이므로
(b)
만약
을 만족시킨다. 한편,
이제
을 만족시키고, 각
그러므로
이므로,
10. Let
(문제에선 a.e.=가 아니라 그냥 =로 나와있는데 a.e.=가 맞는 것 같음)
Prove that TFAE:
- (1)
f - (2)
∑k∈Z2km(Fk)<∞ - (3)
∑k∈Z2km(E2k)<∞
Verify the following assertions:
is integrable on
Also,
is integrable in
증명:
By the definition of
Therefore (1) iff (2).
Now observe that
Since all the entries have nonnegative value, we can alternate the order of summation. Therefore
So we have that
which implies (2) iff (3).
Now let's determine the integrability of
(a가 negative일땐 쉬우므로 a가 양수인 걸 가정.)
For
Therefore
The second one is similiar to the first one.
14. We evaluate the constant
(a) For
(b) By similar methods, show that
(c) The result is
증명
(a) Remark. Lemma 3.8 states that ''the volume below the graph'' is equal to ''the integral of the function''. So, this is immediate.
(b) See below.
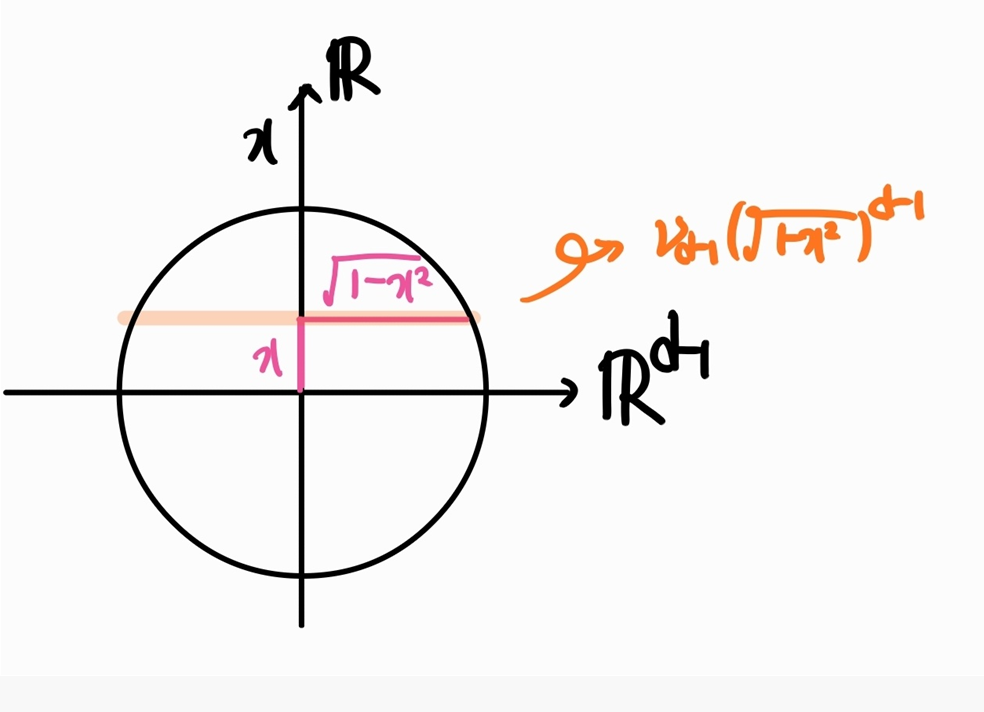
(c) Substitute
Therefore, by (b),
considering
18. Let
증명
푸비니 정리에 의해, 고정된 상수
따라서, 다음이 성립하며
Problem 3.
A sequence
A sequence
Prove that for a sequence of integrable functions
Is the converse true?
증명
Cauchy in sequence는 그냥 소개해준 것 같고.. (문제랑 아무 상관 없고) 귀류법을 써서 증명하기 위해 Converge in measure를 논리기호로 써보면
이고 이걸 부정하면
이다. 저기서
이므로
반대로, 역의 반례를 들어보도록 해보자. 다음 함수
의 경우,
김 모 양의 입시일정으로 7번 문제를 따로 풀게 되었다.
7. Let
증명.
다음을 보이면 Countable Additivity를 이용해서 문제가 증명되므로, 다음은 이 문제의 충분조건이다.
The graph of
이 명제는 다음을 통해 보여진다.
이때
따라서,
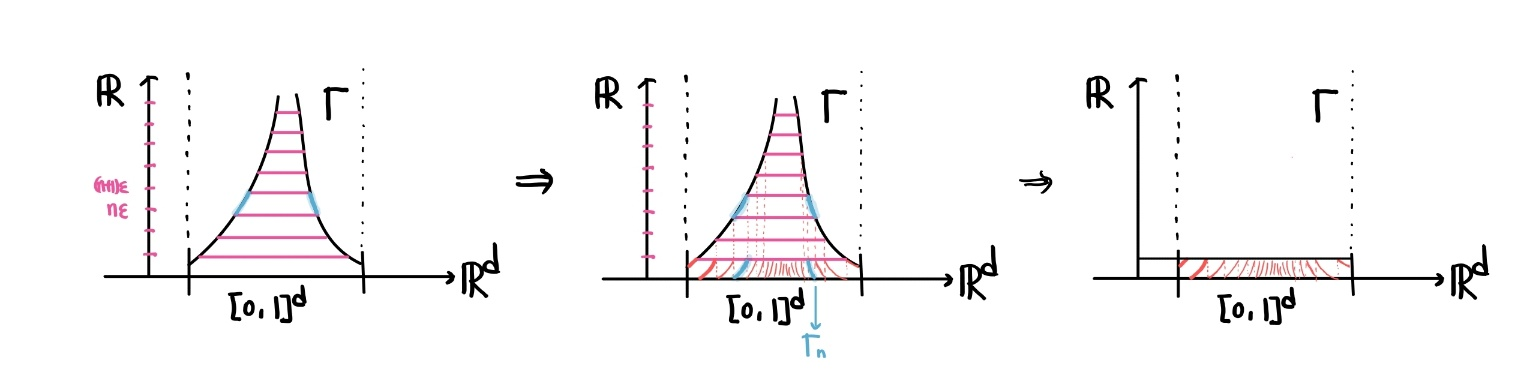
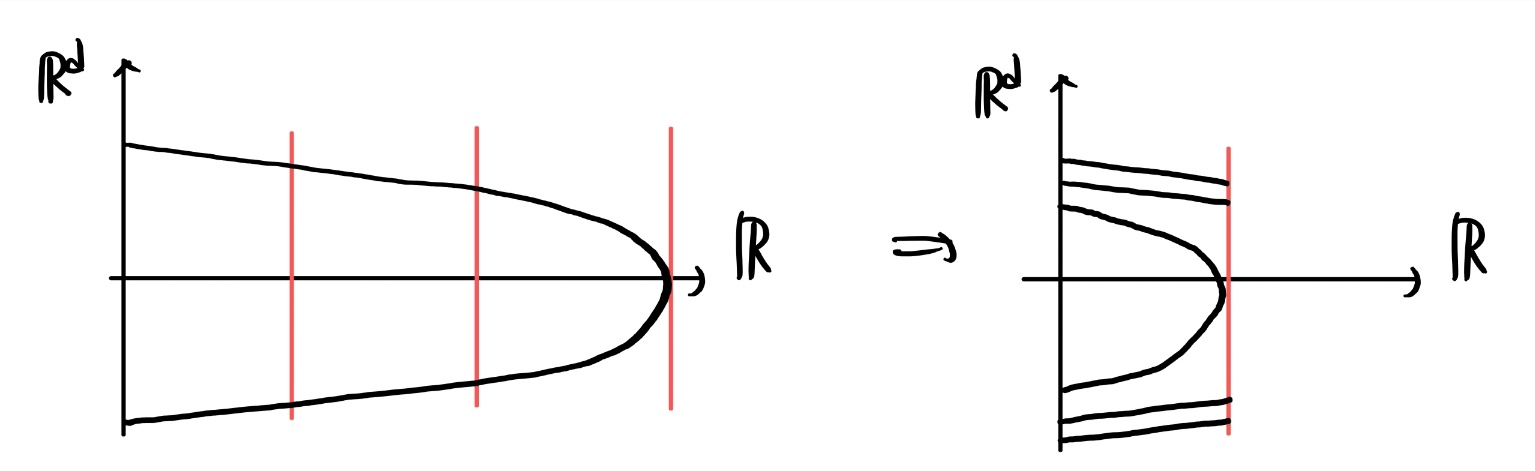
함수 그래프를 변형시키는게 마치 삼단봉을 집어넣는 것 같다고 이야기 했더니 몰매를 맞을 뻔 했다.

'기타 > 시험 관련' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Stein 3장 연습문제 (0) | 2024.04.29 |
|---|---|
| 대수학1 중간고사 대비 (0) | 2024.04.24 |
| 미다체 중간고사 복기 (0) | 2024.04.22 |
| 해석학1 중간고사1 복기 (0) | 2024.04.21 |